Pre-Requisites#
The following configurations should be applied to the platform to use Arthur’s Backup and Restore capabilities:
Arthur must be configured to use external object storage, specifically, AWS S3
The access to external storage must be configured using IRSA annotations
In order to use IRSA annotations, the cluster must be deployed using Amazon EKS
If the above are not true/possible for your deployment, please reach out to Arthur Support.
Configuring Velero#
The only component that needs to be installed separately from Arthur to perform backup and restores is Velero. Instructions are provided below for setting up Velero to store backups in S3 using IRSA. The general overview of the installation is as follows:
Setup permissions for Velero
Install Velero
Confirm Velero is installed and configured correctly
Configure the Backup Storage Destination to point to S3
Velero permissions#
Generate the below policy which will grant Velero the necessary permissions:
$ cat > velero-policy.json <<EOF { "Version": "2012-10-17", "Statement": [ { "Effect": "Allow", "Action": [ "ec2:DescribeVolumes", "ec2:DescribeSnapshots", "ec2:CreateTags", "ec2:CreateVolume", "ec2:CreateSnapshot", "ec2:DeleteSnapshot" ], "Resource": "*" }, { "Effect": "Allow", "Action": [ "s3:GetObject", "s3:DeleteObject", "s3:PutObject", "s3:AbortMultipartUpload", "s3:ListMultipartUploadParts" ], "Resource": [ "arn:aws:s3:::${BUCKET}/*" ] }, { "Effect": "Allow", "Action": [ "s3:ListBucket" ], "Resource": [ "arn:aws:s3:::${BUCKET}" ] }, { "Effect": "Allow", "Action": [ "kms:CreateGrant*", "kms:ReEncrypt*", "kms:GenerateDataKey*", "kms:Encrypt*", "kms:DescribeKey*", "kms:Decrypt*" ], "Resource": "*" } ] } EOF$ aws iam create-policy \ --policy-name velero-perms \ --policy-document file://velero-policy.json
Attach this IAM policy to the IAM role that the Arthur service account (IRSA) assumes
$ aws iam attach-role-policy \ --role-name <IRSA-Role-name> \ --policy-arn <policy-ARN>
Note
Arthur highly recommends that your EBS volumes are encrypted with KMS. In addition to giving Velero the permission for KMS, please make sure that the IAM roles assumed by Arthur service account also have access to KMS so the restored encrypted volumes can be re-attached. If you’re using separate KMS keys on the cluster you backed-up and the cluster you’re restoring to, the EBS volume snapshots must be copied with the new KMS key so the new cluster can work with the snapshots.
Install Velero#
Velero can be installed on the Kubernetes cluster using helm.
Generate a
velero-valuesfile as follows (taken from the official source with defaults removed for brevity):$ cat > velero-values.yaml <<EOF resources: requests: cpu: 500m memory: 128Mi limits: cpu: 1000m memory: 512Mi initContainers: - name: velero-plugin-for-aws image: velero/velero-plugin-for-aws:v1.6.1 imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent volumeMounts: - mountPath: /target name: plugins podSecurityContext: runAsNonRoot: true runAsUser: 1000 runAsGroup: 1000 upgradeCRDs: true cleanUpCRDs: false configuration: # Cloud provider being used (e.g. aws, azure, gcp). provider: aws backupStorageLocation: # name is the name of the backup storage location where backups should be stored. name: <insert-bsl-name-here> provider: aws # bucket is the name of the bucket to store backups in. Required. bucket: <insert-s3-bucket-name-here> config: region: us-east-2 volumeSnapshotLocation: # name is the name of the volume snapshot location where snapshots are being taken. Required. name: <insert-vsl-name-here> config: region: us-east-2 # These are server-level settings passed as CLI flags to the `velero server` command. logLevel: debug namespace: <insert-velero-namespace-here> rbac: # Whether to create the Velero role and role binding to give all permissions to the namespace to Velero. create: true # Whether to create the cluster role binding to give administrator permissions to Velero clusterAdministrator: true # Name of the ClusterRole. clusterAdministratorName: cluster-admin # Information about the Kubernetes service account Velero uses. serviceAccount: server: create: true name: velero annotations: eks.amazonaws.com/sts-regional-endpoints: "true" eks.amazonaws.com/role-arn: <insert-IAM-Role-ARN-here> labels: credentials: useSecret: false backupsEnabled: true snapshotsEnabled: true deployNodeAgent: false EOF
Install the Velero helm chart, with the above values file:
$ velero_namespace=<insert-velero-namespace-here> $ helm install velero vmware-tanzu/velero \ --create-namespace \ --namespace $velero_namespace \ --version 3.2.0 \ -f velero-values.yaml
Note
Arthur recommends installing Velero in a different namespace from Arthur, so Velero can be managed separately from Arthur.
Verify Velero Installation#
To confirm that Velero is installed and configured correctly:
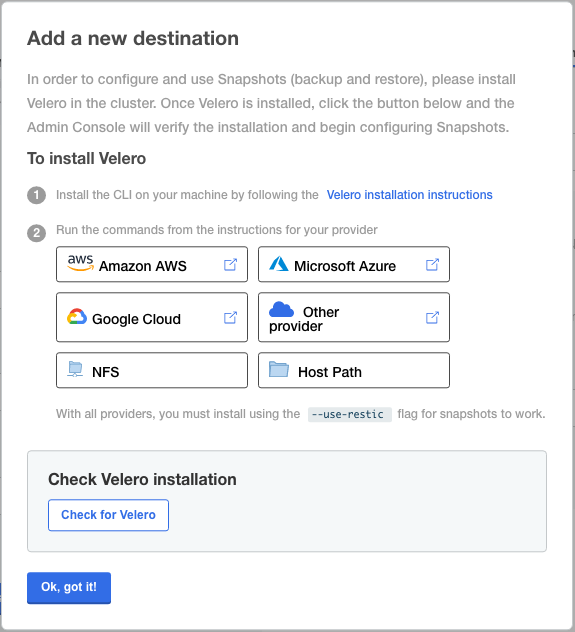
Open the Kots Admin Interface and navigate to the “Snapshots” tab
Click the “Check for Velero” button (see the screenshot below)
Validate the Backup Storage Location#
The Backup Storage Location is a Velero resource that points to the S3 Bucket where backups will be stored. Use kubectl to validate connectivity/access to AWS S3, which should say “Available”.
$ velero_namespace=<insert-velero-namespace-here>
$ kubectl get backupstoragelocation -n $velero_namespace
Please do not proceed until the Backup Storage Location is Available.
Configuring clickhouse-backup#
Configuring clickhouse-backup to store backups in remote storage (eg: S3) can be done in the Admin Console. Once your cluster is setup for Backup and Restore, you should see the “Enable OLAP Database Backup Capabilities” option in the “OLAP Database” section.
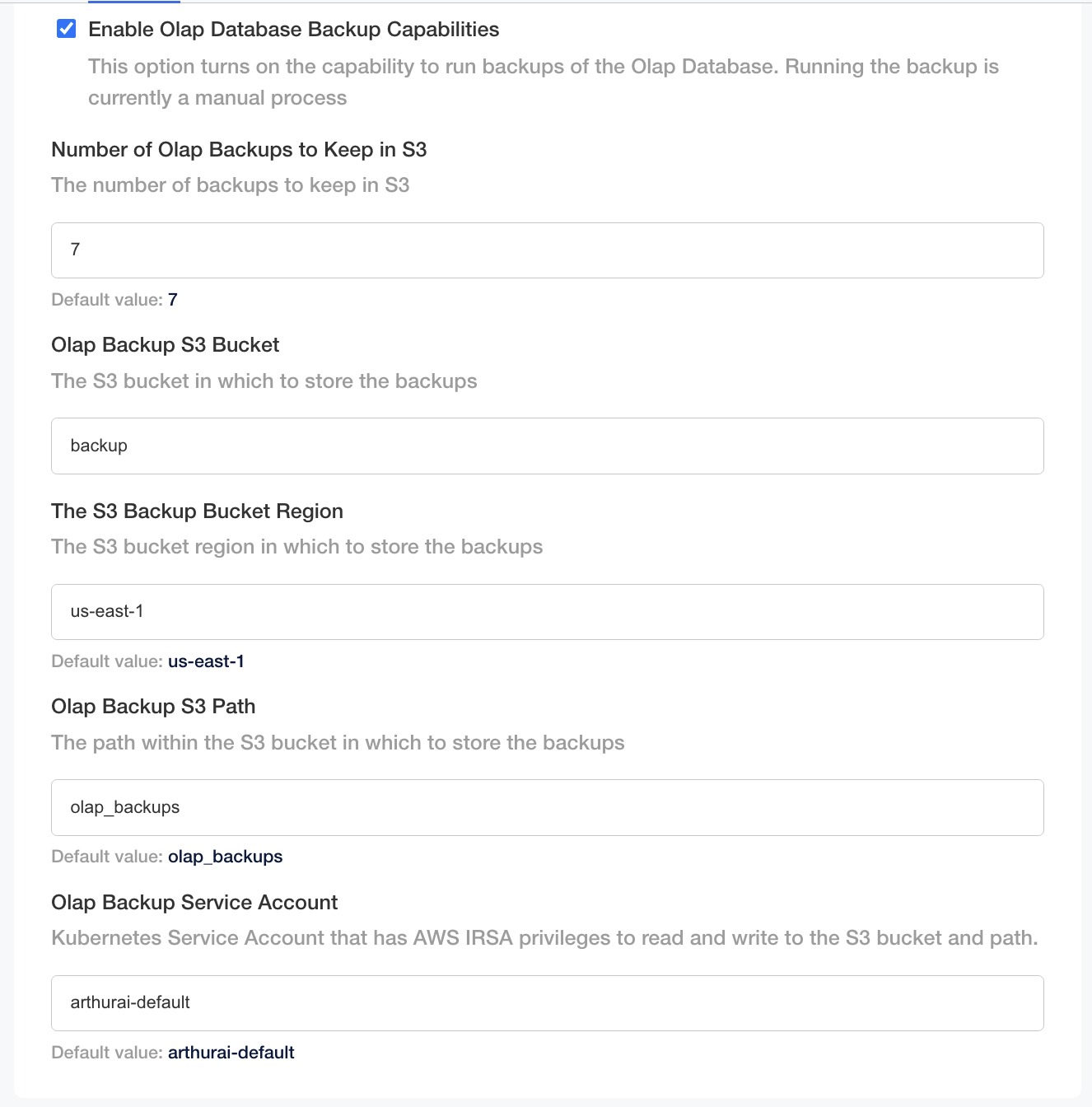
Ensure that:
The configuration that points to the bucket is correct
The Bucket Name
The Bucket Region
The ServiceAccount is the same ServiceAccount that you’ve configured with the IRSA annotation (if you are not sure, enter the default value)
The IAM Role that you are using for the IRSA annotation has the appropriate permissions to read/write/list from the S3 bucket
The S3 Path is where you want to be storing backups